On April 2, U.S. President Donald Trump is scheduled to announce new tariffs that are expected to apply to all countries. Previously, Trump had introduced several tariffs on imports of steel, aluminum, automobiles, and goods from China. These tariff policies aim to protect the U.S. manufacturing industry, create more jobs, and reduce the trade deficit. However, these policies may also lead to higher prices for consumers in the U.S. and trigger tensions in global trade.
What is a Tariff Policy?
Tariffs are taxes imposed on goods imported from other countries. They are usually calculated as a percentage of the product’s value. For example, if an item costs $10 and the tariff is 25%, then the consumer or company importing the item must pay an additional $2.50 as an import tax.
Tariff Payment Process:
- Companies importing the goods are required to pay the tariff to the government.
- Companies may choose to pass on part or all of the additional costs to consumers by increasing product prices.
Why is Trump Implementing Tariffs?
Tariffs are one of the key policies in Trump’s economic vision. The main reasons behind this decision include:
- Reducing the Trade Deficit: Trump aims to reduce the U.S.’s large trade deficit, especially with countries such as China and the European Union. In 2024, the U.S. recorded a trade deficit of $213 billion with the European Union, which Trump described as an “atrocity.”
- Encouraging Local Product Purchases: Trump argues that these tariffs will encourage U.S. consumers to buy domestically made products, which in turn could boost the U.S. economy and create more jobs.
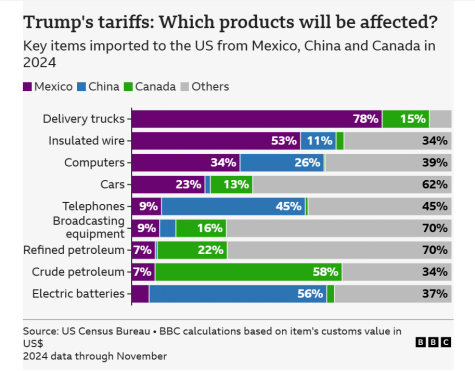
- Pressuring Other Countries: Tariffs are also used as a tool to compel countries like China, Mexico, and Canada to stop sending illegal migrants and drugs to the U.S.
Although Trump does not rule out the possibility of a recession due to this tariff policy, some U.S. officials, including Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick, have stated that the tariffs are “worth it” despite the risk of a recession.
Impact of Tariffs on U.S. Consumers
Rising Prices of Goods
Economists predict that these new tariffs will increase the prices of various imported goods for U.S. consumers. Affected products include:
- Alcohol: Such as beer, whiskey, and tequila.
- Food: Including avocados, maple syrup, and other food commodities.
- Automobile Components: For instance, new tariffs on imported cars could increase car prices by $4,000 to $10,000, depending on the type of vehicle.
- Household Appliances: Such as washing machines, which saw a 34% price increase between 2018 and 2023 due to tariffs on steel and aluminum imports.
Apart from price hikes, companies may also reduce the number of imported goods entering the U.S., potentially leading to shortages of some products and further increasing prices for available goods in the market.
Announced Tariffs
Some of the tariffs that have been announced or will be implemented in 2025 include:
- April 2: A 25% tariff on cars imported into the U.S., with an additional 25% tariff on car parts set to take effect in May or later.
- March 12: A 25% tariff on all steel and aluminum imports.
- March 6: An expansion of tariff exemptions for goods traded under the North American Free Trade Agreement, including televisions, air conditioners, and food products like avocados and beef.
- March 5: A tariff exemption for cars produced in North America that meet the continent’s free trade agreement standards.
- February 4: A 10% tariff on goods from China, later increased to 20%.
Responses from Other Countries
Several countries and international trade blocs have responded to Trump’s tariff policies by imposing retaliatory tariffs on U.S. goods, raising concerns about a potential global trade war. Some of the measures taken by these countries include:
- European Union: Announced tariffs on U.S. products worth €26 billion (approximately £22 billion), effective April 1, with full implementation by April 13. Affected products include ships, bourbon, motorcycles, and steel and aluminum.
- China: Imposed tariffs of 10-15% on some U.S. agricultural goods and on sectors such as aviation, technology, and defense.
- Canada: Introduced a 25% tariff on U.S. steel and aluminum, along with other selected goods. The country is likely to introduce additional tariffs on April 2.
- Mexico: While Mexico has delayed retaliatory tariffs, it remains in discussions on countermeasures against U.S. tariff policies.
Global Impact
Trump’s tariffs not only affect the U.S. economy but also have the potential to escalate tensions in global trade. Trade wars involving major economies like the U.S., China, and the European Union could disrupt global supply chains and negatively impact many countries that rely heavily on international trade.
These tariff policies could reshape global trade dynamics, worsen trade relations with many countries, and negatively impact U.S. consumers through higher prices. While the goal is to protect domestic industries, the long-term effects on both the global and domestic economy remain uncertain.
